Jaggery, also known as Gur, is a sweetener made from sugarcane juice. Even though jaggery is frequently used to make a variety of sweet meals, you might not be aware of whether it is safe to eat while pregnant.
In addition to being a healthier substitute for refined sugar, jaggery is a great source of vital minerals like iron and mineral salts that are good for the developing fetus and the mother. Jaggery is a rich dietary source that promotes a healthy pregnancy if used in moderation.
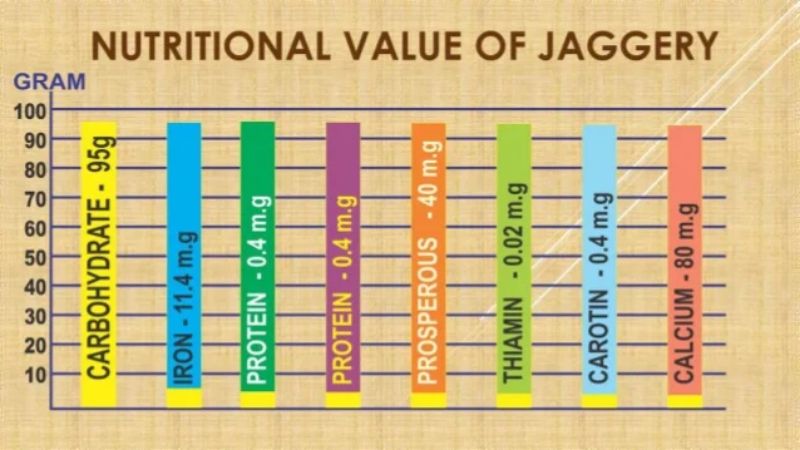
Nutritional Information
Jaggery, a “powerful sweetener” derived mostly from sugar cane and occasionally date palm, may be familiar to you.
While only 10% of high-quality jaggery contains glucose and fructose and less than 5% contains minerals, over 70% of it is composed of sucrose. Depending on the raw materials used (palm or cane), the nutritional value may vary.
Calcium (40 to 100 mg), potassium (1,056 mg), magnesium (70 to 90 mg), sodium (19 to 30 mg), iron (10 to 13 mg), phosphorus (20 to 90 mg), zinc (0.2 to 0.4 mg), manganese (0.2 to 0.5 mg), copper (0.1 to 0.9 mg), and chloride (5.3 mg) are all present in half a cup (100 grams) of jaggery. There are very trace amounts of several vitamins.
Benefits Of Jaggery During Pregnancy
- Prevents Anaemia: The woman will avoid anemia, puerperal septicemia, low birth weight, and premature delivery if she consumes adequate iron during her pregnancy. Pregnancy-related jaggery consumption lowers the risk of anemia and raises the red blood cell count. It supports the immune systems of expectant mothers and is an incredibly fast-acting energy source.
- It aids in blood pressure control: During pregnancy, accurate blood pressure monitoring is essential. You can avoid kidney problems, stroke, and cardiovascular disease by including jaggery in your daily diet. Jaggery helps absorb nutrients and contains less salt than table sugar.
- Blood cleaning and water retention: A little jaggery every day during pregnancy would assist rid the body of waste and toxic substances. This will protect the life developing inside of you.
If a pregnant woman has fluid retention, jaggery may help. The high potassium content of jaggery helps maintain weight by preventing fluid buildup. Jaggery also lowers the risk of pulmonary edema. - Rich in antioxidants: jaggery is a powerful antioxidant. As a result, it safeguards the developing fetus’s health and helps avoid cellular damage. Moreover, the antioxidant properties strengthen the mother’s immune system and help avoid common illnesses.
- Reduces Joint Pain: Apart from its numerous other applications, pregnant women might benefit greatly from jaggery due to its beneficial benefits on their bones and muscles. Jaggery can help reduce the pain and stiffness associated with spinal arthritis.
How Can You Incorporate Jaggery Into Your Pregnancy Diet?
Jaggery is a versatile sweetener with a wide range of possible uses.
- Combine with liquids, such as tea or milk.
- Add it to desserts like puddings.
- Add some peanuts or shredded coconut to make it sweeter.
- Add to cakes and toffee-based baked items.
- Made from sugar cane or date palm, jaggery is a sweetener with a higher sucrose content than glucose. When consumed in moderation, jaggery during pregnancy is safe to consume. It is also a better substitute for sugar and helps maintain a balanced diet. Jaggery can provide you with some of the iron you need on a daily basis. The nutritious value of jaggery might vary depending on its makeup. However, since consuming too much of anything can result in weight gain, moderation is crucial.
Possible Side Effects of Jaggery During Pregnancy
Jaggery during pregnancy may have some health benefits, but as it is essentially sugar without refinement, it is not advisable to consume significant amounts of it.
Additionally, jaggery that is tainted or contaminated may cause issues. Therefore, before incorporating jaggery into your prenatal care diet, proceed with caution.
- Overconsumption of jaggery will raise the calorie count and may cause weight gain.
- After an hour of intake, the glycemic index of jaggery is 84.1. If you already have gestational diabetes, the sugars in jaggery may cause your blood sugar levels to rise, which could be hazardous.
- Microbes may be present in impure jaggery.
Tinydale is on YouTube, Click here to subscribe for the latest videos and updates.
Follow Us: Facebook | Instagram | Twitter | Youtube | Pinterest



